MidPO: Dual Preference Optimization for Safety and Helpfulness in Large Language Models via a Mixture of Experts Framework
Large Language Models (LLMs) need to be both helpful and safe, but achieving both is a major challenge. We propose MidPO, a Mixture of Experts (MoE) framework that fine-tunes two specialized experts for safety and helpfulness and uses a dynamic routing mechanism to adaptively balance them, outperforming existing methods.
The Safety vs. Helpfulness Dilemma #
Aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) is a delicate balancing act. Current methods often force a trade-off between being helpful and being safe.
- Online alignment methods (like RLHF) can be overly cautious, leading them to refuse safe, harmless prompts. This is known as the “excessive safety” or “over-refusal” problem.
- Offline alignment methods (like DPO variants) often fail to adapt, sometimes providing helpful but harmful responses to unsafe prompts.
📄 Paper 📁 Code (to be released)
What We Built: The MidPO Framework #
Our framework, MidPO (Mixture of Experts Dual Preference Optimization), addresses this challenge with two core components:
- Two Specialized Experts: Instead of a one-size-fits-all model, we train two distinct experts: a Safety Expert and a Helpfulness Expert. We use our novel Single-Preference Enhanced DPO (SPE-DPO) method to make each expert highly proficient in its domain.
- A Dynamic Routing Mechanism: A smart “router” analyzes the user’s prompt and adaptively decides how much to listen to the Safety Expert versus the Helpfulness Expert. This allows the model to be cautious with unsafe prompts but open and helpful with safe ones.
- Efficient Offline Alignment: The entire framework is built on an offline alignment process, making it more stable and computationally efficient than online RLHF-based methods.
Method & System #
- Framework Overview MidPO first transforms a base LLM into two specialized experts using LoRA fine-tuning with our SPE-DPO loss functions. Then, it freezes the experts and trains a dynamic router that learns to combine their contributions effectively for any given prompt, achieving a superior balance between safety and helpfulness.
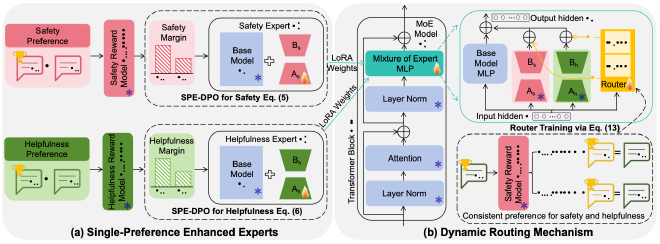
- Single-Preference Enhanced Experts (SPE-DPO)
The foundation of MidPO is creating highly specialized experts. Our proposed SPE-DPO method is designed for single-preference optimization. By introducing a homogeneous preference margin, it amplifies the distinction between good and bad responses within a single category (e.g., safe vs. unsafe), making the experts more effective than if they were trained with standard DPO.
- Dynamic Routing Mechanism
This is where the magic happens. The router analyzes the input prompt and assigns a weight to the Safety and Helpfulness experts. For an unsafe question (e.g., “How to do X illegal thing?”), it gives more weight to the Safety Expert. For a safe question (e.g., “How do I make my wife laugh?”), it prioritizes the Helpfulness Expert. This adaptive approach ensures the final response is context-appropriately safe and helpful.
Data & Settings #
Base Model: We built MidPO on top of the widely used Alpaca-7B model.
Datasets: We trained and evaluated MidPO on three popular benchmarks:
PKU-Safe RLHF , Do Not Answer , and Wildguard Mix.
We compared MidPO against strong baselines, including
Safe RLHF (an online method) and MODPO (an offline method), ensuring a fair comparison by using the same base model for all methods where possible.
Representative Findings #
Our comprehensive evaluation showed that MidPO sets a new standard for balancing safety and helpfulness.
Unprecedented Balance MidPO consistently achieves the highest scores for both safety and helpfulness across all three datasets, significantly outperforming all baselines. Other methods either excel at one while failing at the other or are mediocre at both.
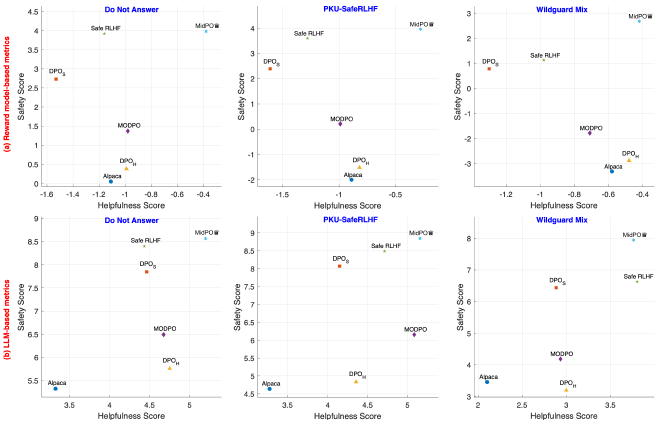
Superior Experts and Routing #
Better Experts: Our experts, fine-tuned with SPE-DPO, demonstrated superior single-preference performance compared to experts trained with vanilla DPO.
Effective Routing: Ablation studies confirmed the crucial role of the dynamic routing mechanism. Removing it led to a significant drop in both safety (19.25% win rate) and helpfulness (13.62% win rate).
Citation #
Reference (arXiv Preprint):
Yupeng Qi, Ziyu Lyu, Min Yang, Yanlin Wang, Lu Bai, Lixin Cui. 2025. MidPO: Dual Preference Optimization for Safety and Helpfulness in Large Language Models via a Mixture of Experts Framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.02460.
BibTeX
Code snippet
@misc{qi2025midpo, title={MidPO: Dual Preference Optimization for Safety and Helpfulness in Large Language Models via a Mixture of Experts Framework}, author={Yupeng Qi and Ziyu Lyu and Min Yang and Yanlin Wang and Lu Bai and Lixin Cui}, year={2025}, eprint={2506.02460}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.CL} }